ALTERNATIVE INVESTMENT FUNDS

Vinay Mehta
Vinay Mehta is a qualified and experienced Company Secretary, Lawyer, and Commerce Graduate by and has a rich experience of almost a decade in Compliances, Governance, FEMA Matters, Regulatory reporting, Corporate Secretarial matter and deep insight and niche in AIF related matters.
WHAT IS ALTERNATIVE INVESTMENT FUND ?
Alternative investment fund , means any fund established or incorporated in India in the form of a Trust or a Company or a Limited Liability Partnership or a body corporate which is privately pooled investment vehicle which collects funds from investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investing it in accordance with a defined investment policy for the benefit of its investors; and is not covered under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Mutual Funds) Regulations 1996, Securities and Exchange Board of India (Collective Investment Schemes) Regulations 1999, or any other regulations of the board to regulate fund management activities.
- Family Trust The Family Trust is a popular vehicle in estate planning. You know your family best, and a family trust can help you customize how you provide for your family, both during your lifetime and after your death.
- ESOP Trust An ESOP Trust is an entity established by companies to hold shares for the purpose of the ESOP program and /or to hold shares on behalf of eligible employees participating in the ESOP program.
- Employee Welfare Trusts (EWT) Employee Welfare Trusts (EWT) are established to cater to employee welfare needs such as funding child education, medical expenses and extra ordinary expenses not covered under compensation.
- Holding Company A Holding Company is a type of financial organization that owns a controlling interest in other companies, which are called subsidiaries.
- Securitization Trust The Securitization Trust is the financial vehicle used in the process of securitization and plays a crucial role in converting various types of liquid financial assets into marketable securities.
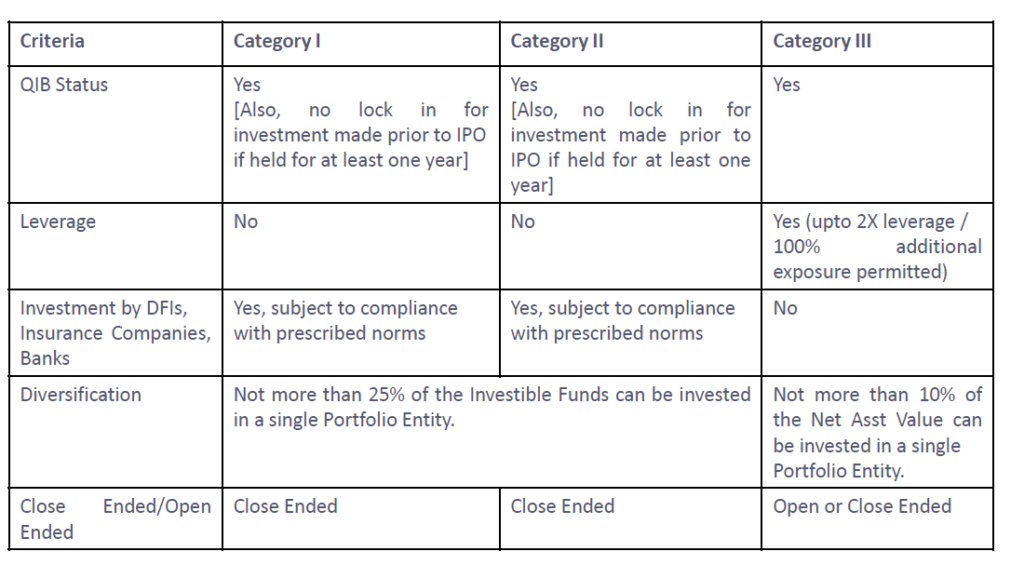
- AIFs primarily serve high-net-worth individuals (HNIs), institutional investors, and other accredited investors.
- The funds are pooled.
- With AIFs, the SEBI-mandated minimum investment amount is INR 1 crore
- The number of investors involved in any AIF scheme cannot be more than 1000 (except Angel Funds)
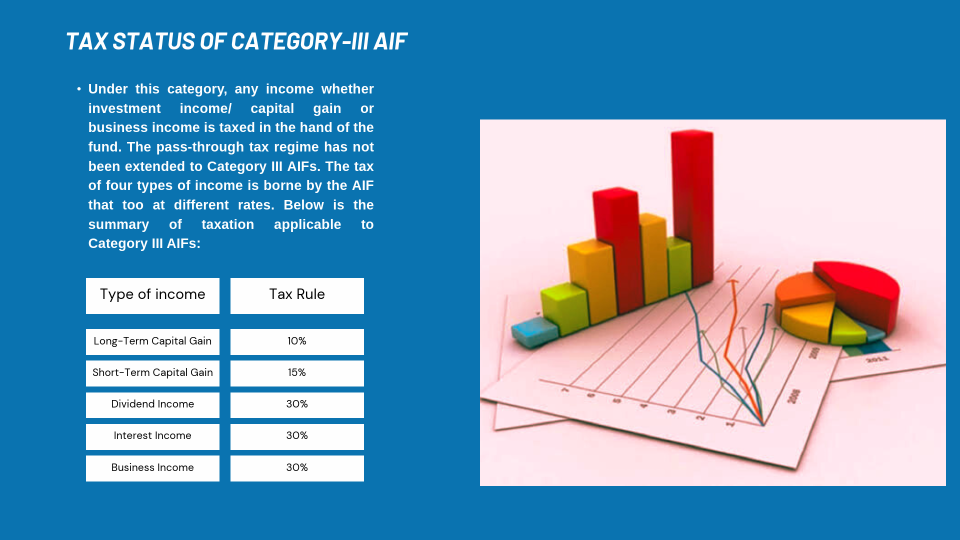
- Category III AIFs are not granted pass-through status and hence income earned by such fund is subject to taxation at the fund level itself.
- Category-I and II AIFs are usually closed-ended, while Category-III AIFs can be open or closed-ended. In the case of closed-ended funds, the minimum tenure is 3 years.
- PMS is offered by expert portfolio managers or management services firms to high-net-worth individuals (HNIs) as well as retail investors.
- The funds are not pooled.
- With PMS, INR 50 lakhs is the minimum SEBI-mandated amount.
- There are no limitations when it comes to the number of investors.
- Capital Gains and other incomes accumulated in PMS is taxed in the hands of investor as per their applicable tax rate
- There is no fixed tenure for securities when investing through PMS.
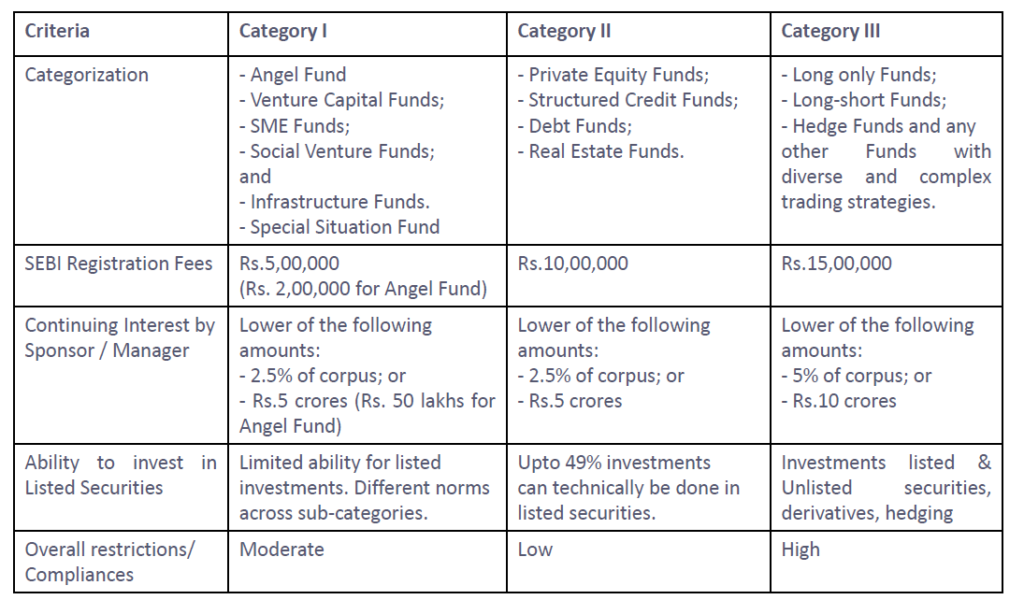
➤ Types of AIF. According to the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), AIFs are classified into three broad categories:
- Category-1.
- Venture capital Funds.
- Infrastructure Funds.
- Social venture Funds.
- Category -2
- Private Equity funds
- Fund of funds
- Debt Funds
- Category -3
- Hedge funds
- Private Investment in Public Equity funds
- Open ended Funds These funds do not have any fixed maturity period. Investors can conveniently purchase and sell units at the Net Asset Value (NAV), which is declared daily.
- Close ended Funds It have a fixed maturity period. It has fixed capital commencement from investors, means, they raise specific amount of capital during a limited fundraising period.
- Evergreen Funds. Evergreen funds are a type of investment vehicle that allows investors to make long-term investments in private companies. Unlike traditional private funds, which typically have a fixed lifespan of approximately 10 years, evergreen funds do not have a fixed end date.
- A category-I AIF of a particular sub-category may invest in the units of the same sub-category of Category-I AIFs. However, this investment condition is subject to the further restriction that Category-I AIFs are not allowed to invest in the units of Fund of Funds.
- Category-I AIFs shall not borrow funds directly or indirectly or engage in leverage except for meeting temporary fund requirements for more than thirty days, on not more than four occasions in a year and not more than 10% of its investible funds.
- Venture Capital Funds.
- Infrastructure Funds.
- Angel Funds.
- Social Venture Funds.
- Venture capital funds Who seek private equity stakes in start-ups and small- to medium-sized enterprises with strong growth potential. These investments are generally characterized as very high-risk/high-return opportunities.
- Infrastructure funds Is a privately offered or publicly listed fund that invests directly or indirectly in infrastructure and associated industries. Examples of direct
- Angel funds It refers to a money pool created by high net-worth individuals or companies (generally called as angel investors), for investing in business start ups. They are a sub-category of venture capital funds with strict focus on startups, while venture capital funds generally invest at a later stage of development of the investee company.
- Social venture Funds To provide seed-funding investment, usually in a for-profit social enterprise, in return to achieve an outsized gain in financial return while delivering social impact to the world.

Examples of this category are as follows:
- Fund of Funds
- Debt Funds
- Private Equity Funds
- Fund of Funds A FOF aims at diversifying the risk of a single fund by investing in several types of funds. An investor with limited capital can invest in one FOF and get a diversified portfolio consisting of, for example, bonds, gold, equity, and debt
- Debt Funds A debt fund is a that invests in fixed income instruments, such as Corporate and Government Bonds, corporate debt securities, and money market instruments etc. That offer capital appreciation. Debt funds are also referred to as Income Funds or Bond Funds.
- Private Equity Funds A private equity fund (abbreviated as PE fund) is a collective investment scheme used for making investments in various equity (and to a lesser extent debt) securities according to one of the investment strategies associated with private equity.
Category-III AIF
Category-III AIFs are those funds which give returns under a short period of time. These funds use complex and diverse trading strategies to achieve their goals. There is no known concession or incentive given towards these funds specifically by the government. Examples of this category are as follows:
- Hedge Funds
- Private Investment in Public Equity Funds
- Hedge funds
A Hedge fund is a pooled investment fund that holds liquid assets and that makes use of complex trading and risk management techniques to improve investment performance and secure returns from market risk.
- Private investment in public equity
Private investment in public equity (PIPE) is when an institutional or an accredited investor buys stock directly from a public company below market price. Because they have less stringent regulatory requirements than public offerings, PIPEs save companies time and money and raise funds more quickly.
HOW PRIVATE EQUITY FUNDS WORK ?
- A Private Equity Fund has Limited Partners (LP), who typically own 99% of shares in a Fund and has limited liability and General Partner (GP), who owns 1% of shares and have full liability. The GP is also responsible for executing and operating the investment.
- The LP‘s will generally be institutional investors or high net worth individuals that can commit substantial amounts of money to the fund for up to 10-12 years.
- The GP will be responsible for the day-to-day management of the fund and will appoint all the various service providers to assist with the management of the fund.
HOW PRIVATE EQUITY FUNDS MAKE MONEY ?
- Management fees traditionally consist of a firm charging to LP 1.5% – 2.0% on committed capital / NAV / called capital
- Carry interest :- LP will get the part of the additional return generated above the hurdle rate
- During an initial deal, private equity firms will often charge their portfolio companies a transactional fee worth 1% of the deal amount.

SEBI AIF REGULATIONS,2012
- The AIF Regulations prohibit solicitation or collection of funds except by way of private placement. While the AIF Regulations do not prescribe any thresholds or rules for private placement, guidance is taken from the Companies Act,2013.
- Listing Units of close ended Alternative Investment Fund may be listed on stock exchange subject to a minimum tradable lot of one crore rupees. Such Listing of Alternative Investment Fund units shall be permitted only after final close of fund or scheme.
- SEBI has mandated dematerialization of existing physical units as well as mandated to issue units in dematerialized form.
- SEBI has mandated to dematerialized its investment made in the portfolio companies.
- First closure should be done within 1 year from SEBI Approval or refile with SEBI with Merchant banker.
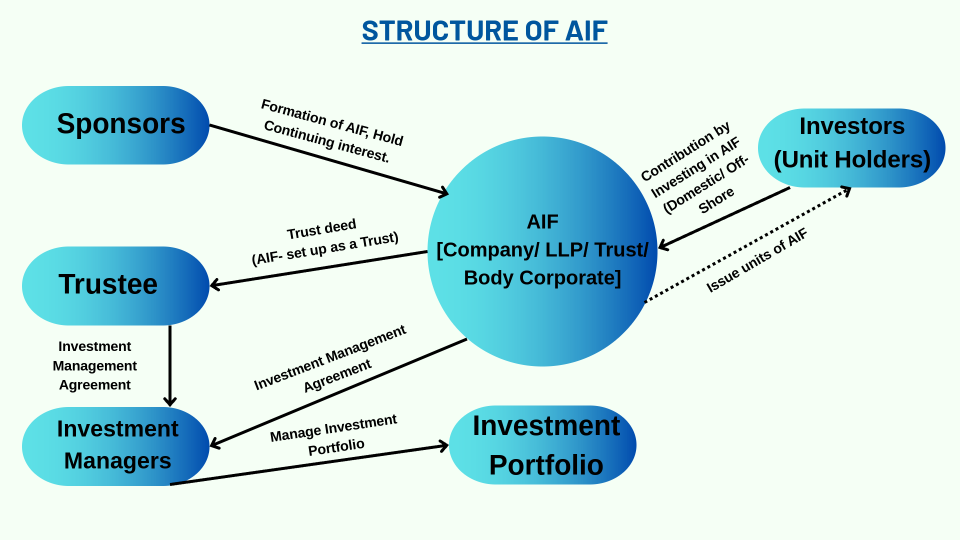
Structure And Stakeholders of AIF

Trustee
- The Trustee is appointed to manage the Trust fund/ property of the Trust in accordance with the Indenture. The Trustee has appointed the Investment Manager and delegated its function of managing and administering the Trust fund in accordance with the Investment Management Agreement.
- The Trustee shall ensure compliance with the Regulations and submitting reports to SEBI on the occurrence of any violation of the Regulations.
- The Trustee shall be responsible for such other duties as specified under the indenture. the Investment Manager and Trustee of the fund shall ensure compliance by the fund with the code of conduct as specified under the Regulations.
Sponsor
- Sponsor / Manager is aligned with the interest of the investors in the AIF, the AIF Regulations require that the Sponsor/ Manager shall have certain continuing interest in the AIF which shall not be through the waiver of management fees.
- For Category-I & II AIFs, such interest must be not less than two and half percent of the corpus or five crore rupees whichever is lesser and for category-III AIFs the interest must not be less than five percent of the corpus or five crore rupees whichever is lesser and for category-III AIFs the interest must not be less than five percent of the corpus or ten crore rupees, whichever is lesser.
Investment manager.
- The Investment Manager shall enter into an Investment Management Agreement with the Trustee in terms of which it will manage the affairs of the Trust and the Fund in accordance with the powers delegated by the Trustee and in accordance with the Applicable Laws.
- The Investment Manager will also be reponsible for the Investment program of the Fund.
Custodian
- The Sponsor or Manager of an AIF is required to appoint a custodian registered with the Board (SEBI) for the safekeeping of the AIF’s securities.
- A Custodian, which is an associate of the Sponsor or Manager, can only act as a Custodian under certain specified conditions.
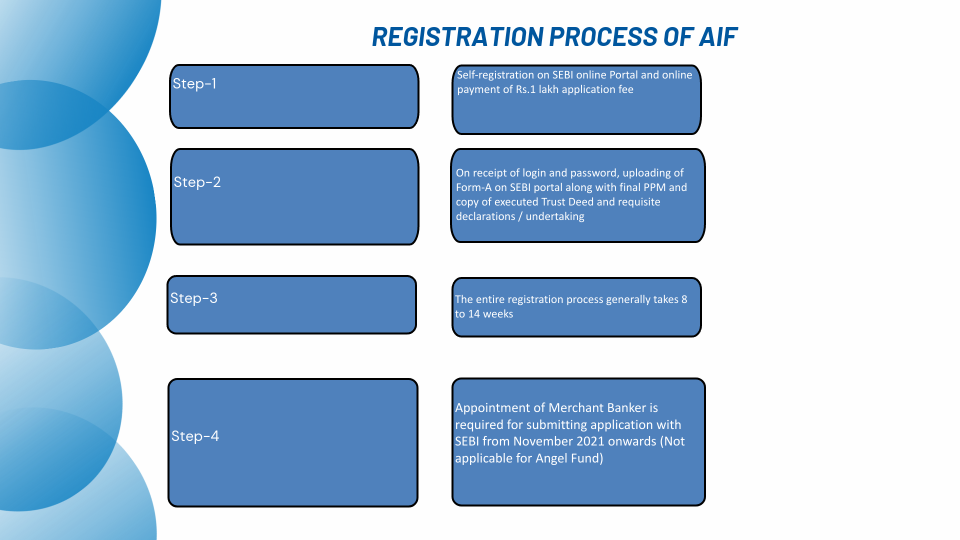
Registration process of AIF
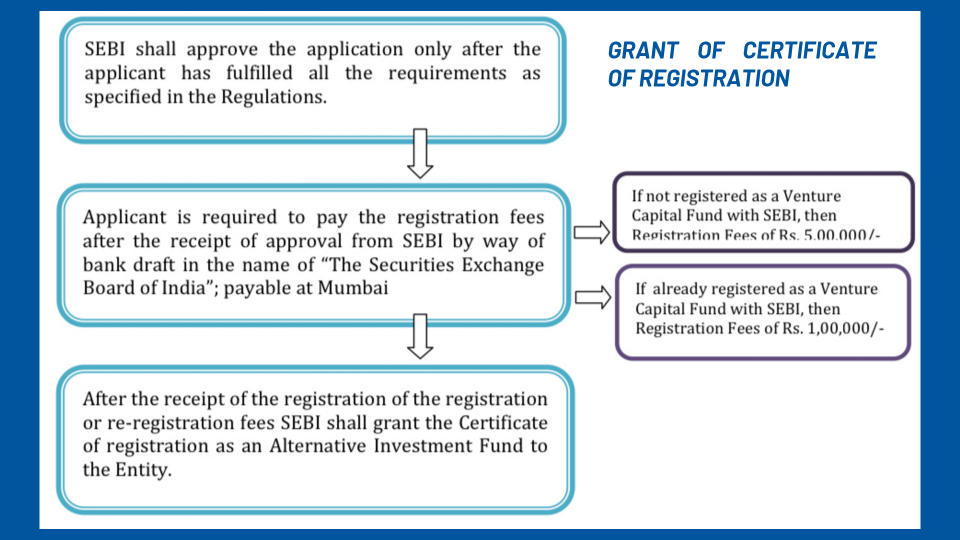
GRANT OF CERTIFICATE OF REGISTRATION
- Memorandum of Association or Article of Association (in case of company)
- LLP Deed (in case of LLP).
- Trust Deed (in case of Trust)
- Contribution Agreement
- Investment management Agreement
- Private placement Memorandum
- Each category of AIF is a different investment vehicle therefore it is taxed differently. As such, it is important for investors to understand the income tax implications of AIFs.
- Income (other than business income) from Category I and II is taxed in the hand of the investor as per their applicable tax rate whereas for Category III income is tax-free in the hands of the investor because Category III AIFs have not been accorded a pass-through status and as such onus to pay the tax lies with the fund. Let’s take a closer look at the tax regulations associated with AIFs.
- The Finance Act of 2015 introduced a special taxation regime under which Category I and II AIFs have been granted a pass-through status. Pass-through means that the income generated by the fund will be taxed in the hands of the investor and not at the fund level. Here, the tax liability on the income generated from the investment is borne by the investor.
Tax Status of Category -3 AIF